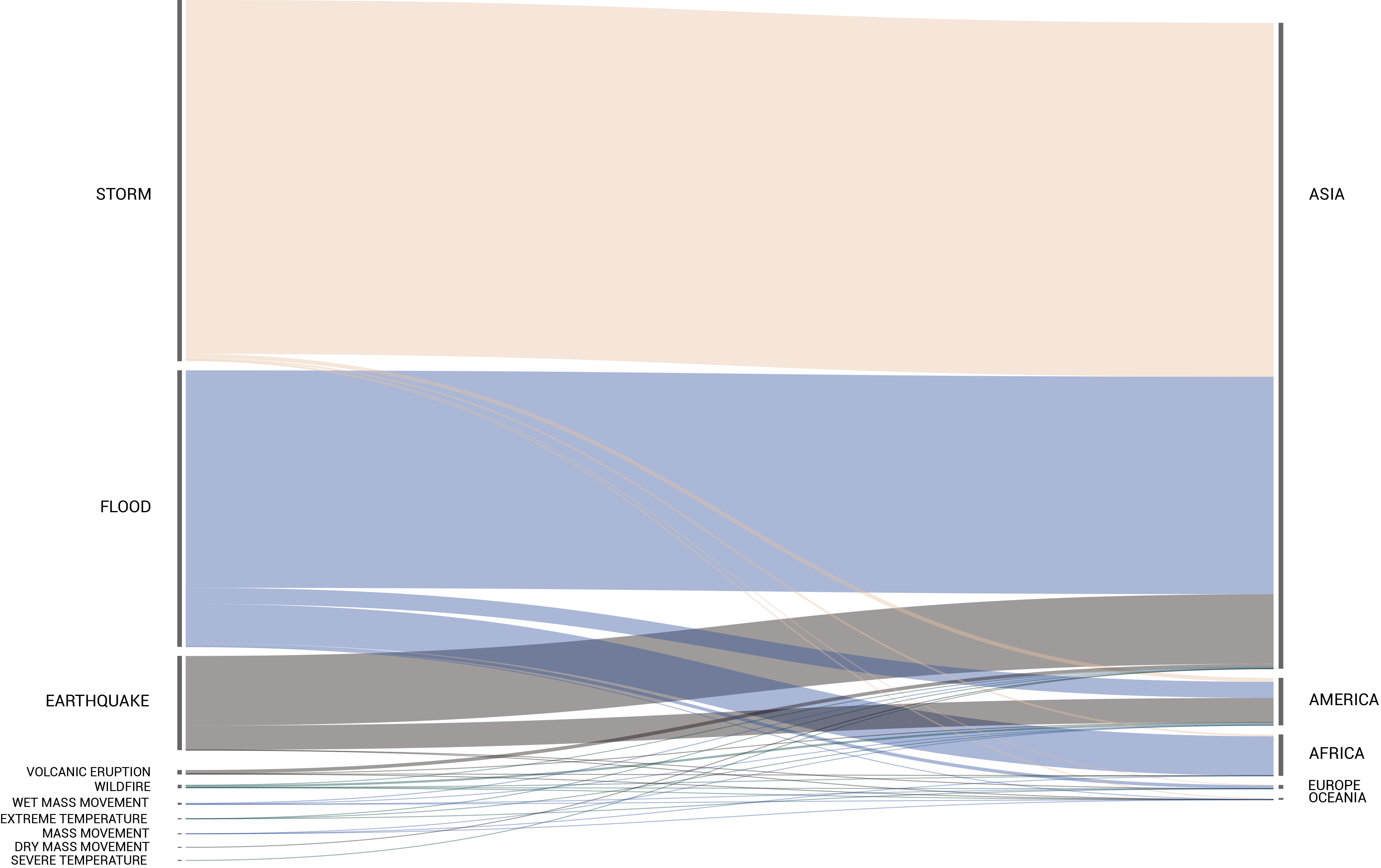
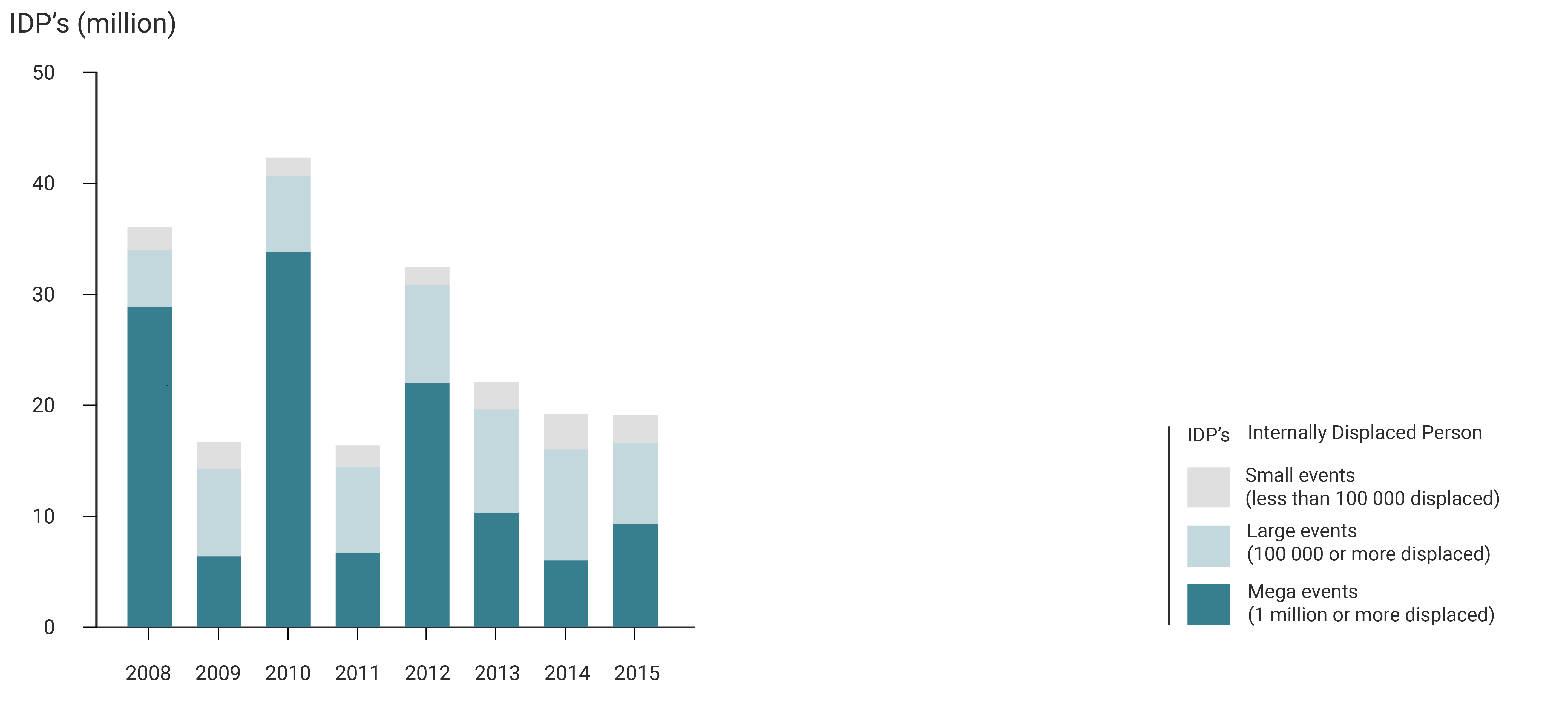
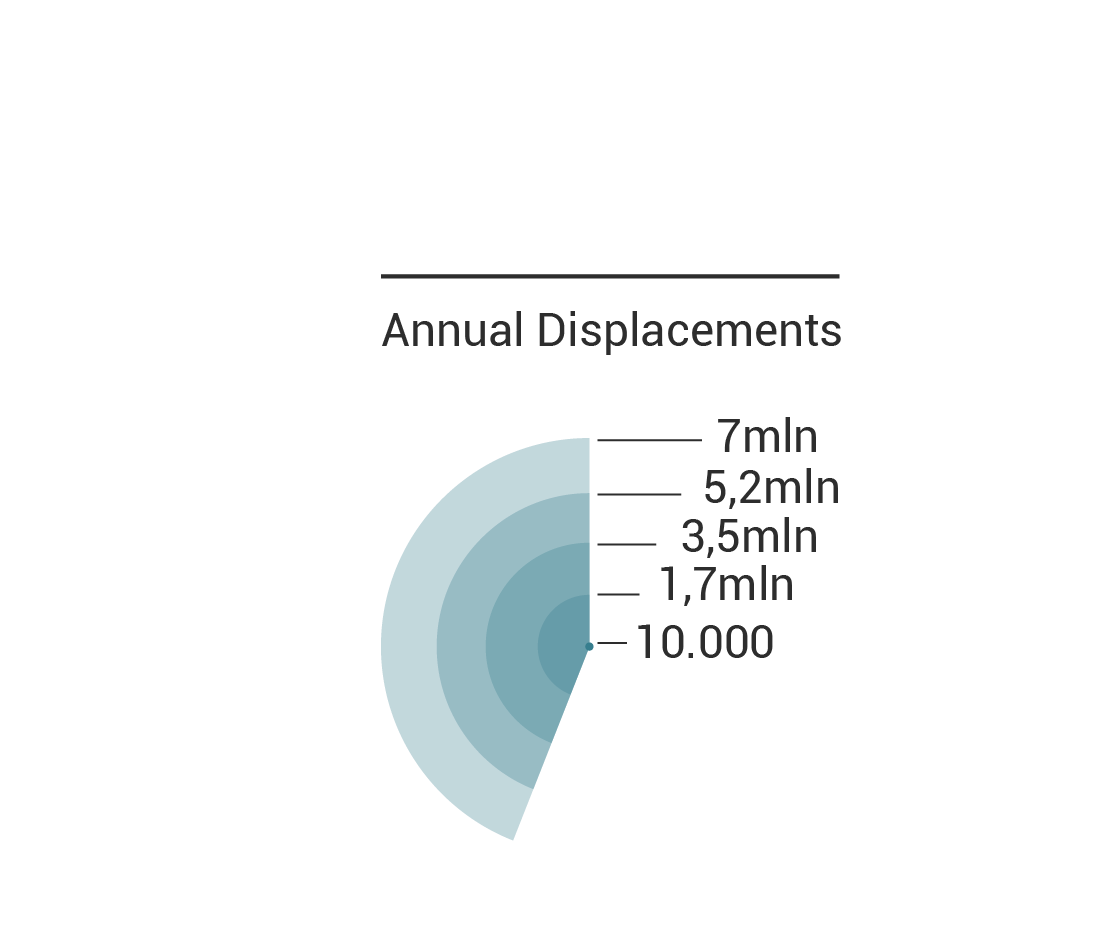
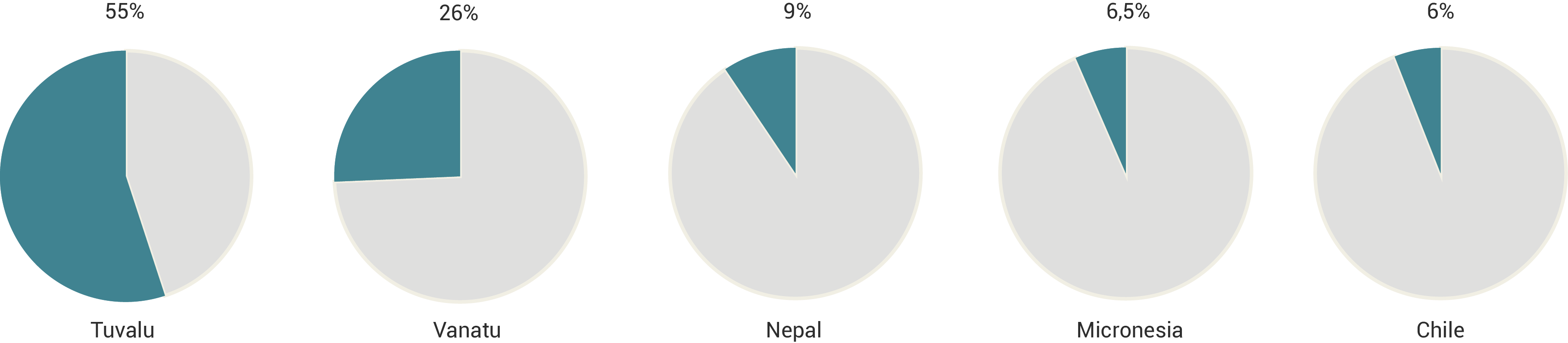
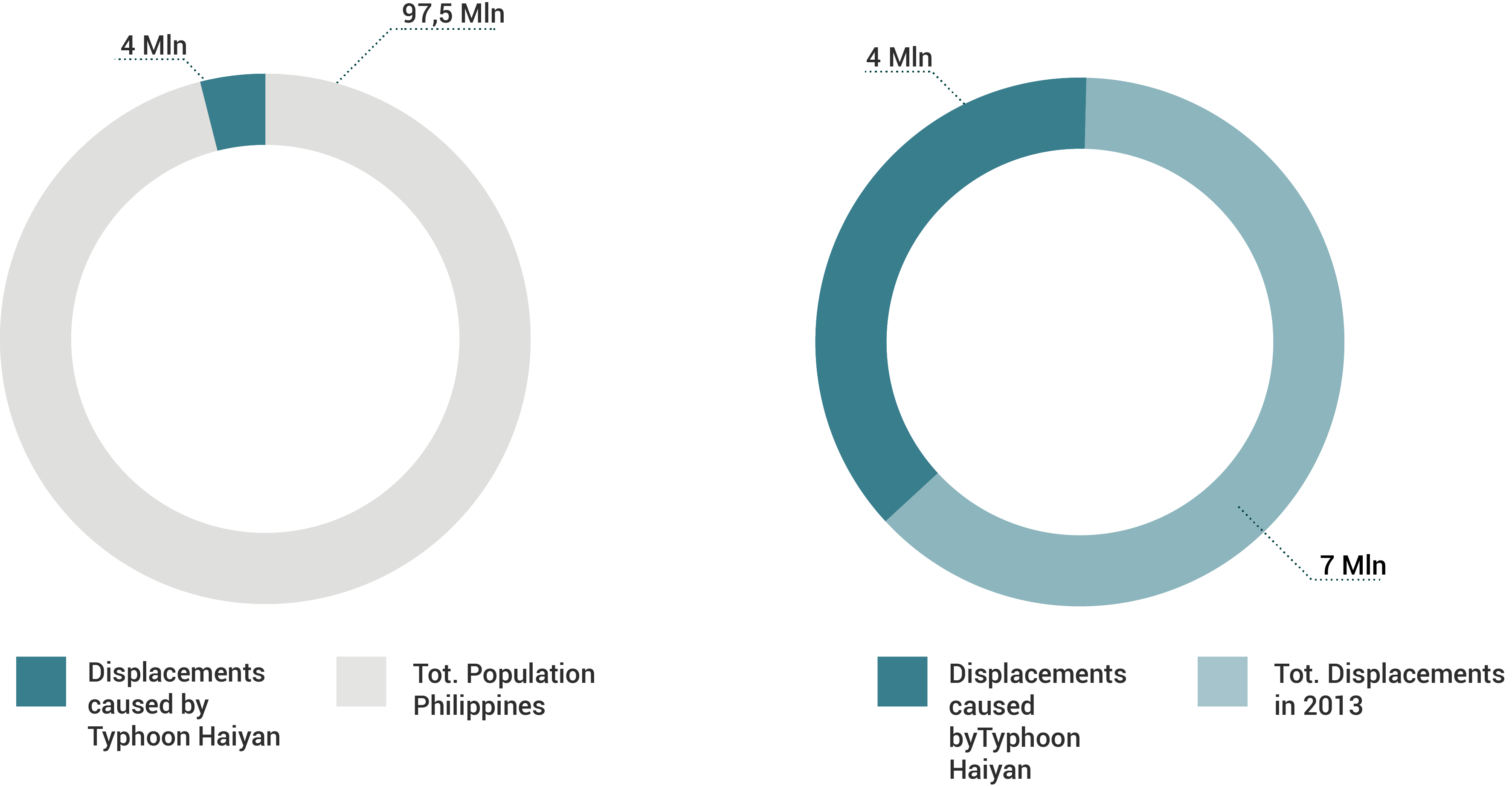
Today, almost all the evacuated people doesn’t cross the national boarders. That means that even if the problem remains inside the country, it becomes even more difficult to trace the migration flow. Moreover, the problem is being studied since 1970 but not before 2008 they had begun to gather data.
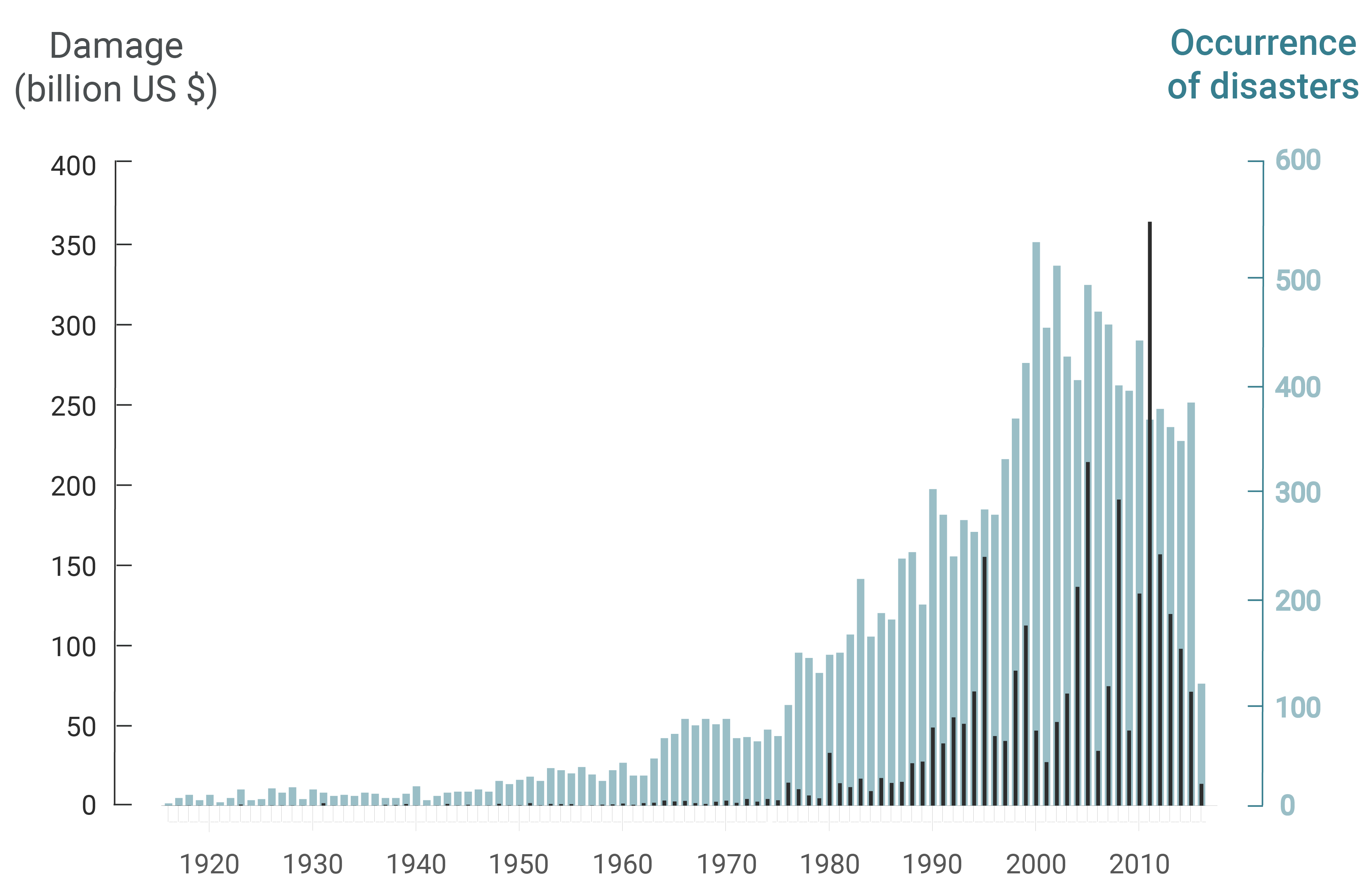
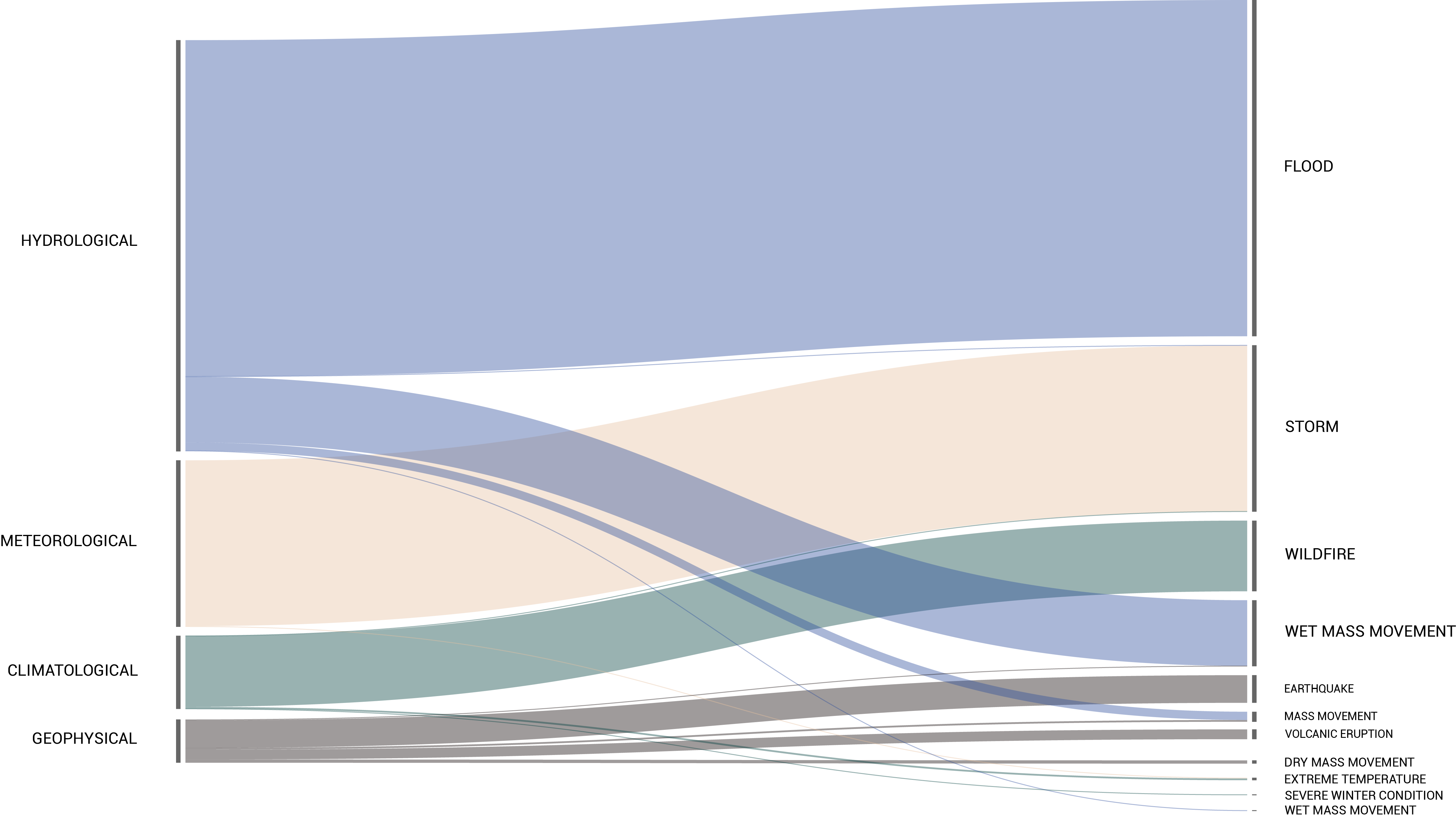
Over the years, the intensity of the natural disasters increases dramatically, creating millions of migrants worldwide. The environmental events, especially the
« mega events », let the affected country in an unstable situation. After that they need emergency plan but also quick and sustainable operations on a socio-economic matter.
Inside the vulnerable countries, this instability can increase and create conflict as well as displacements beyond the boarders. Preparation, reaction time and coordination among close nations are key factors in order to to deal with the consequences of natural disasters and to maintain the balance between populations.
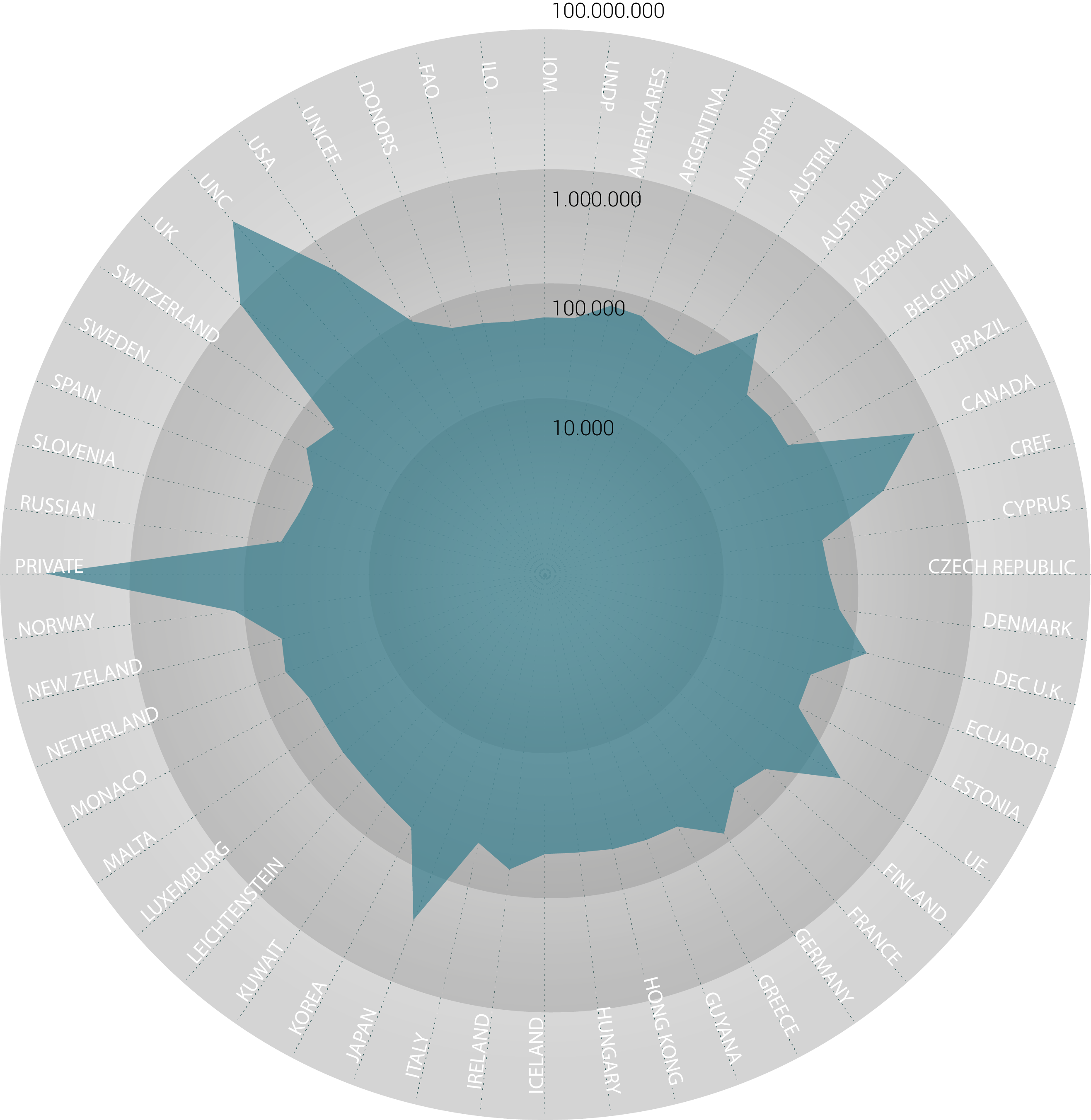
All the databases come from:
D. Guha-Sapir, R. Below, Ph. Hoyois - EM-DAT: The CRED/OFDA International Disaster Database – www.emdat.be – Université Catholique de Louvain – Brussels – Belgium.
IDMC Global Report on Internal Displacement 2016 Disaster Dataset, 11 May 2016.
FTS Financial Tracking Service - https://ftsbeta.unocha.org/ 2016.