A digital currency in which transactions are verified and records maintained by a decentralized system using cryptography, rather than by a centralized authority.
Oxford Languages
Non-fungible tokens or NFTs are cryptographic assets on blockchain with unique identification codes and metadata that distinguish them from each other. Unlike cryptocurrencies, they cannot be traded or exchanged at equivalency.
Investopedia




Want to buy a diamond? But you also want to know exactly where it came from and that it’s the real deal? In real life, you have to trust the people you are buying from, based on what they say and show you.
But blockchain is here to save the day. It can store all the steps about the diamond’s former sales history. It can track and authenticate the diamond, so you can be sure about what you are buying. In the end, you don’t know the resellers in person, but their transactions are tracked within the blockchain system, which makes it nearly impossible to change or forge information about the product.

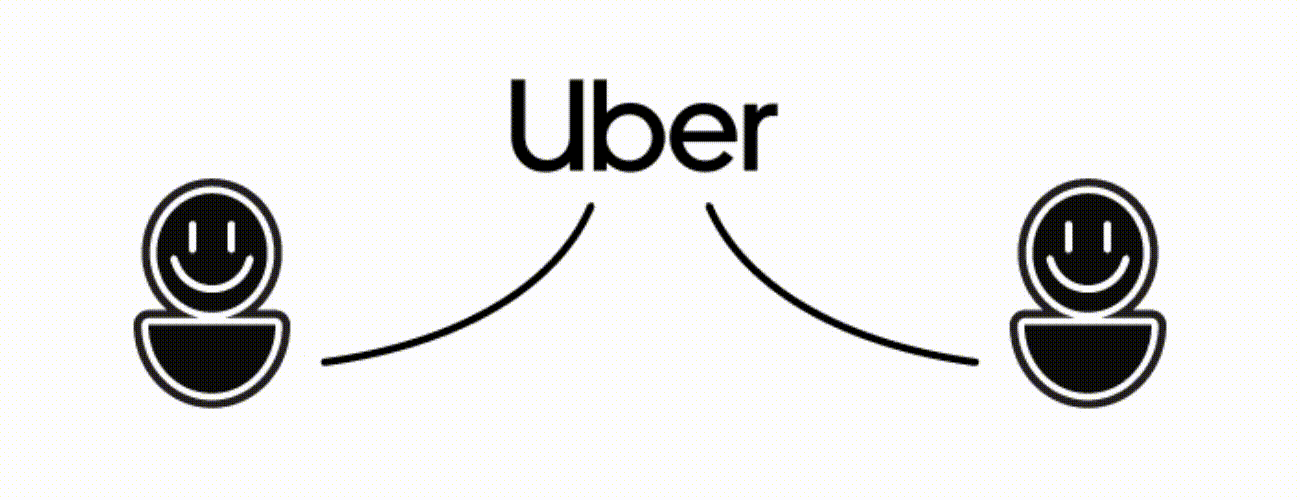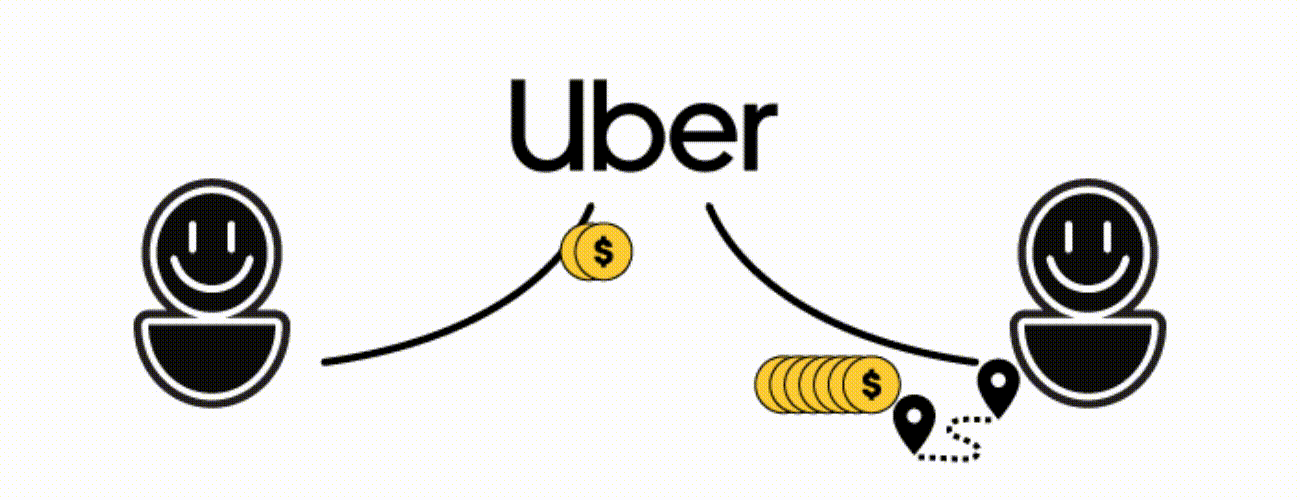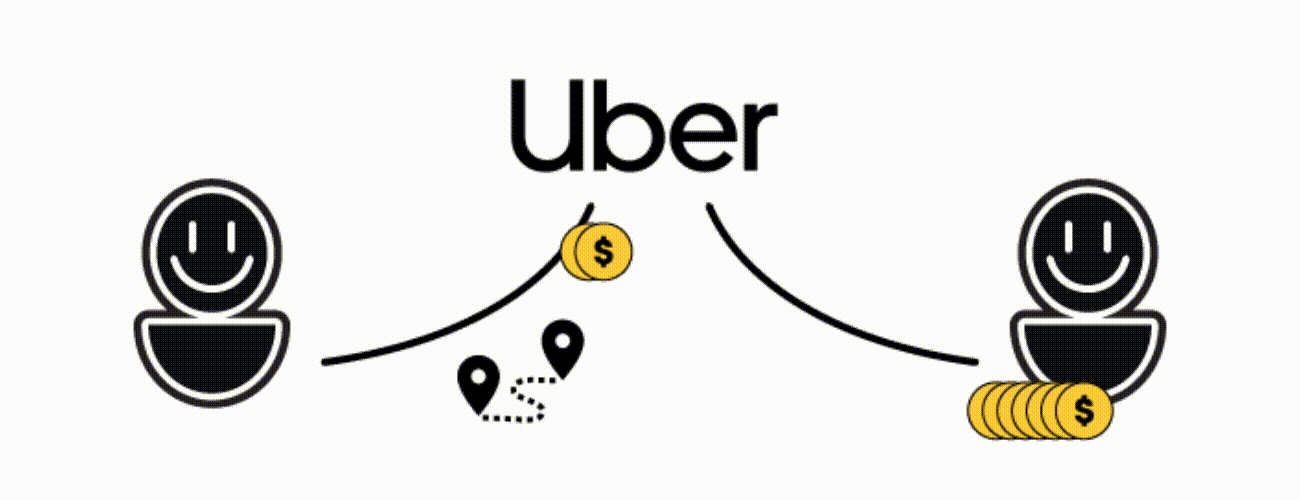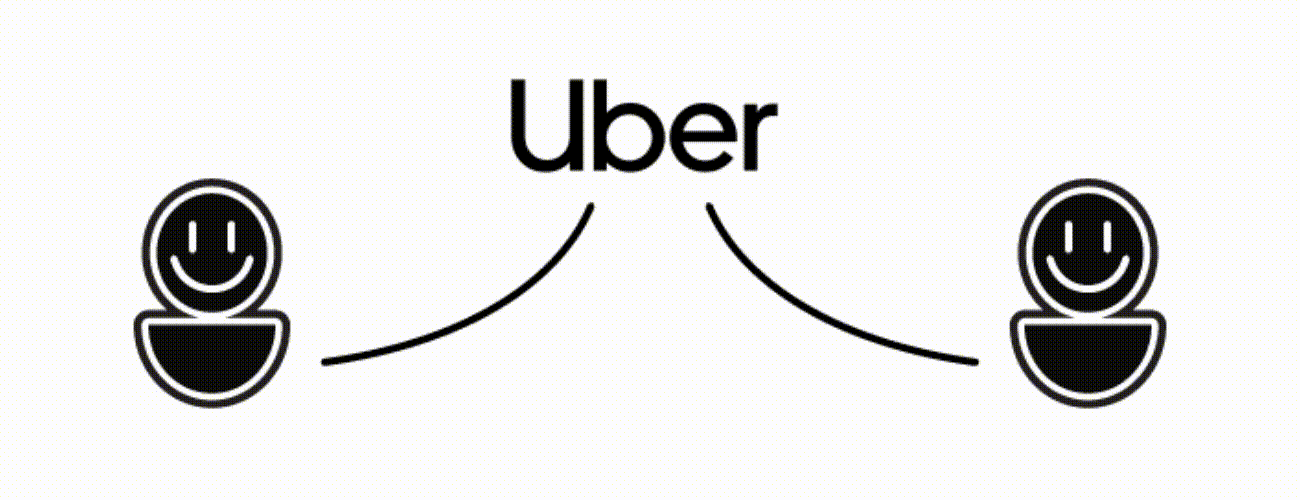
Have you ever used Uber to travel? Then you know that you’re buying a service from another user. The platform just facilitates and secures the process, connecting sellers and buyers. To do so, it charges a fee. In the case of Uber, it’s a service, it works the same with selling products.
But blockchain allows users to trade peer-to-peer, without a middleman. The algorithm verifies if users trade the items they claimed (ex. this specific bag for this specific amount of money) and validates the transaction. No middleman involved.
Have you ever been waiting at the bank? If so, you know how annoying it can be to wait until the person before you is finished.
But blockchain allows you to do it more efficiently. Scalability in regards to blockchain refers to the number of users a network can support and the number of transactions it can process. A strong blockchain network can process a high number of transactions at the same time, therefore it yields an enormous advantage of efficiency.

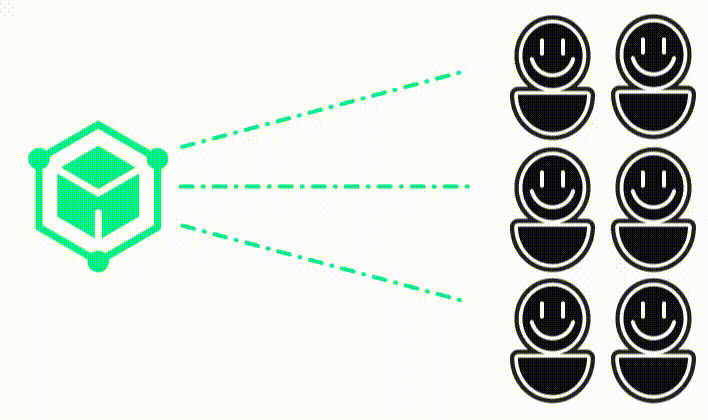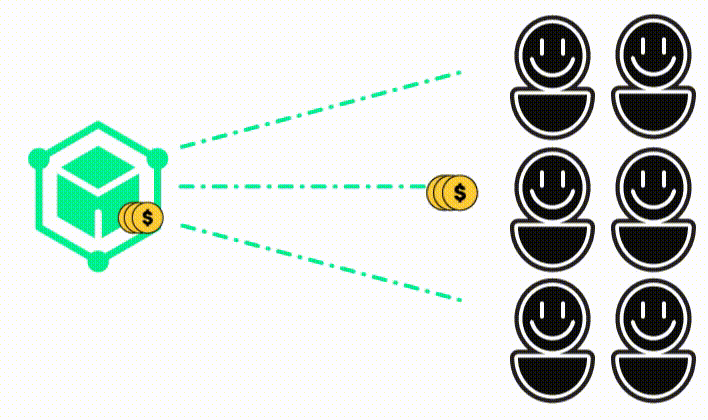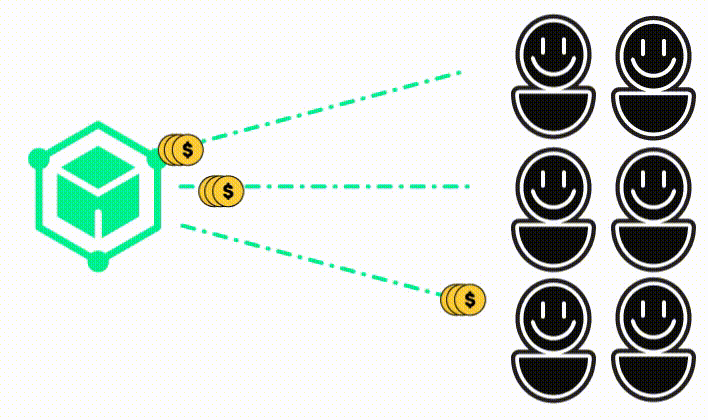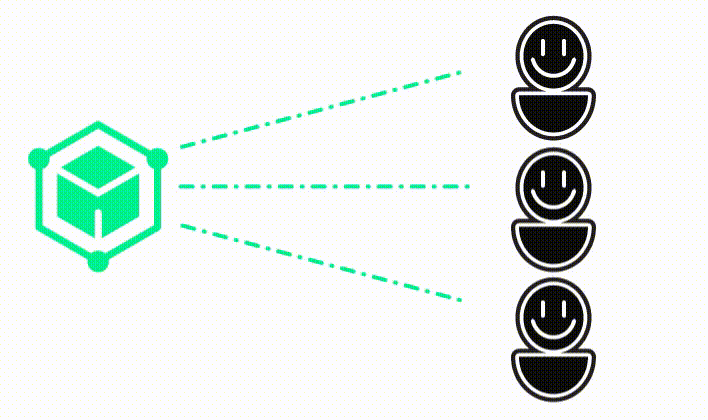
Almost all kind of digital information! For example:
1
This can be any kind of information, but the most common is a record of a transaction. For example, a record that Alice gave Bob 10 dollars.
But it also can be:
2
3
Blockchain is a chain of blocks linked together with unique 64-characters codes called hashes.
Hashes are dependent on information stored on the block. They can’t be calculated and can only be found by random guessing. When a block is added to the blockchain, it has to have the hash of the previous block to connect with it and its own (new) hash to connect with the next block added.
Like the block hash of the first bitcoin block ever created:
000000000019d6689c085ae165831e9
34ff763ae46a2a6c172b3f1b60a8ce26f
What if someone hacks the recorded transaction?
If the transaction changes, then the hash changes too. It would require re-adjusting all the hashes in the chain to make them match again. And this would require too high a power usage.
It differs from blockchain to blockchain. For example, Bitcoin miners are rewarded with
6.25 BTC
for each block mined which is equivalent to
$315 947.50
System makes finding the hash harder, so all miners spend more time finding it. Rewards the first miner who finds the hash.
The one with the stronger computer power is more likely to find the hash quicker and get the reward
System arbitrarily selects a node as a validator for the next block and rewards them. The more money a node “stakes”, the more likely he is to be selected.
The one with the biggest stake is more likely to be selected and get the reward
1 bitcoin ≈ 150 Exahash/s
1 desktop =3300 H/s
(H/s: hashes per second)
530 000 000 000 000 h/s during one year

That's almost 100 I7 processors running non-stop during one year!
a reward for staking of +4.6%
of currency of 1 bitcoin with Cardano
$47,908,926
You also need the knowledge and skills to run a node on the network to be rewarded.
Without these, you could consider delegating your stake to a stakepool where ADA holders manage your stake and make sure you are rewarded!