Description
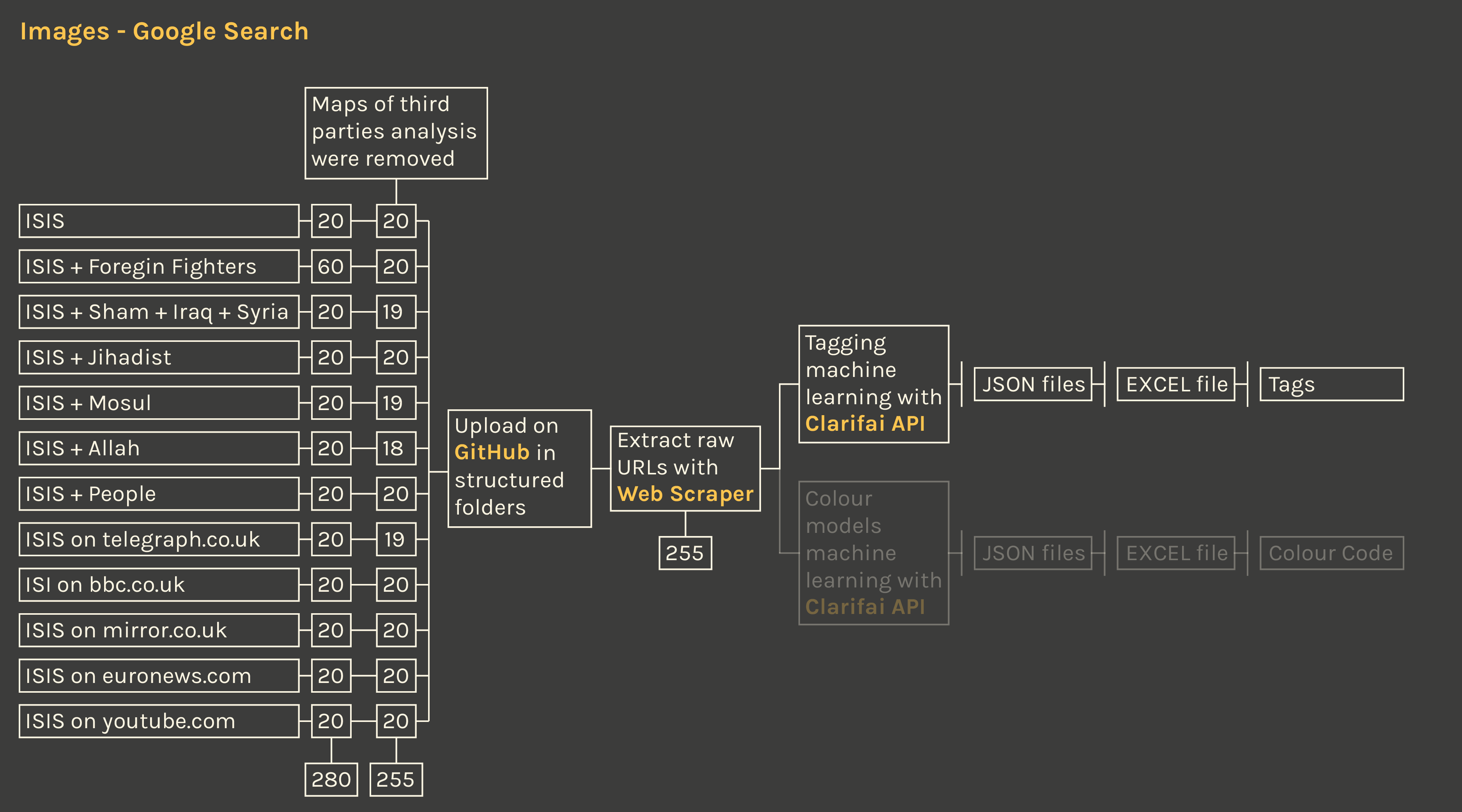
The research of images on Google was done to verify how different media represent the IS in terms of visual content. The research queries were selected in order to compare different sources: (i) “ISIS” on Google images in general; (ii) “ISIS + foreign fighters” from the previous research phase; (iii) “ISIS + Allah”, “ISIS + people”, “ISIS + Sham + Iraq” are the most recurrent words in the official magazines Dabiq and Rumiyah; (iv) “ISIS + Sham + Iraq”, “ISIS + jihadist”, “ISIS + Mosul” are the words where the controversy is focused on Wikipedia based on how many times those words were changed; (v) “ISIS on telegraph.co.uk”, “ISIS on euronews.com”, “ISIS on mirror.co.uk”, “ISIS on bbc.co.uk” to filter results by european media as analyzed for news articles; (vi) “ISIS on youtube.com” to include the image given by a media largerly used for the communication of the IS on the web.
The analysis of the images with the Clarifai APIs allowed tagging through the means of machine learning. The visualization compares the distribution of tags per every query, allowing to locate the similarities and the differences between the images resulting from all the queries. For every tag, the average percentage is highlighted with a yellow line. The bars indicate the query-specific percentage and are yellow when close to the average line and grey when apart. The threshold that determines the color change is 2.5 percentage points, so when the percentage value differs from the average by less than ± 2.5%, the bar is yellow; if the percentage value differs from the average by a greater value than ± 2.5%, then the bar is grey. What stands out is that the predominance of yellow bars signals a strong similarity between all the queries. Hence the visual communication of the media included in the queries is very consistent and gives back a particularly stereotyped image across-the-board despite the different nature of the queries.